New model for chloride ingress in concrete
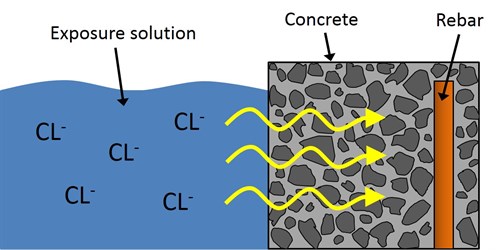
At the Expert Centre for
Infrastructure Materials we have investigated the ingress of
chloride into (1) a number of Danish concrete bridges in marine
environments and (2) concrete blocks placed at the marine exposure
sites in Rødbyhavn (Denmark) and Träslövsläge (Sweden). This has
led to the suggestion of a relatively simple model for chloride
ingress into concrete, which is based on a linear correlation
between the ingress depth (x(cr)) of a given reference
chloride concentration (cr) and the square root of
exposure time:
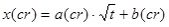
where
a(cr) is a factor of proportionality and
b(cr) is the intercept with the y-axis in a
plot of x(cr) against the square root of
exposure time (t). The value of
a(cr) is an expression of the rate of
chloride ingress of the reference chloride concentration
(cr), while the value of b(cr) is
interpreted as a result of a "fast" initial ingress of chloride
during the first few months (or years) after the first exposure to
the marine environment.
Hydration reaction will typically
still occur during this early period, which means that the
permeability of concrete will be somewhat higher compared to the
same concrete in a more mature state. The initial penetration depth
(b(cr)) could also partly be a consequence of
initial capillary suction of seawater at the time of the first
exposure to a submerged marine environment. Therefore,
b(cr) will most likely be different for the
same concrete depending of the maturity, as well as the moisture
content in the concrete, at the time of the first exposure to
seawater.
The equation above can be
rearranged for t:
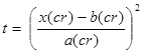
In principle, this equation can be
utilized to estimate the time until initiation of reinforcement
corrosion in a concrete structure, i.e. the duration of the
initiation phase, which is sometimes used as a definition of the
service life of a concrete structure. Such an estimation can be
obtained by equating the value of x(cr) with
the thickness of the concrete cover above the reinforcing steel and
by setting the reference chloride concentration (cr) at a
level equal to the threshold value for initiation of
chloride-induced reinforcement corrosion for the given
concrete.
The research leading to the
suggested chloride ingress model has been carried out with
financial support from the Danish Agency for Institutions and
Educational Grants.